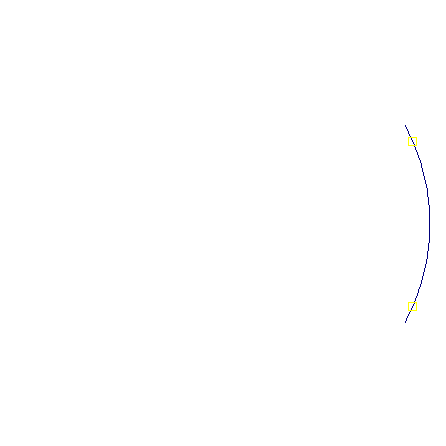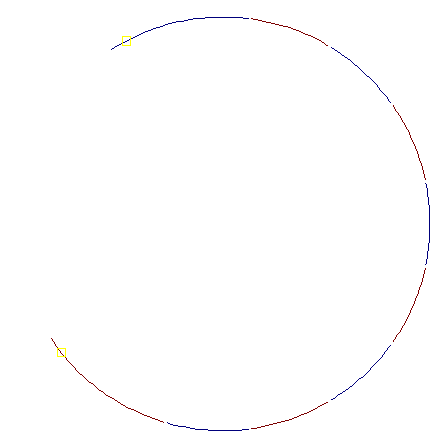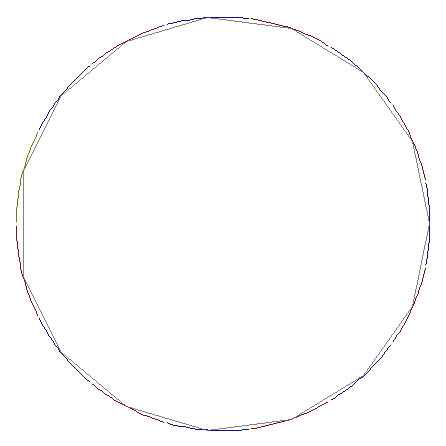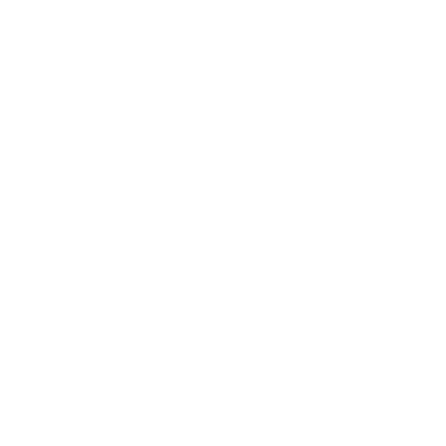

As each new point is added, the intervals around each point are shortened so that the projection of the intervals do not overlap (approximate). Endpoints of the original intervals are then eligible for use to generate a new point. The shortening is done by projecting one interval into the tangent lines at nearby points. The algorithm terminates when there are no longer any endpoints that an be selected.
The result is a set of points on the circle, and a set of edges connecting the centers of intersecting intervals.